
Many of you may have already heard of Intermittent Fasting (IF), a globally popular method for weight loss and improving metabolic processes. Rather than focusing on what to eat, IF is an eating pattern that prioritizes a schedule of when to eat. For example, popular methods include the 16/8 method (fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window) or the 5:2 method (eating normally for 5 days a week and significantly restricting calories for the remaining 2 days). While these methods are convenient and effective for weight loss, everything has its pros and cons. Incorrect fasting can lead to negative health impacts. Let’s explore the benefits, risks, and the right ways to choose a method that suits you.

Effects on the Body
Even if you exercise regularly, fat loss may be slow if your diet is uncontrolled, because the body primarily burns energy from the food you consume. Intermittent Fasting is based on the process where, during the fasting period, the body exhausts its existing sugar stores and begins breaking down stored fat for energy, leading to high weight loss efficiency. These fasting periods trigger significant changes in cells, hormones, and internal organs:
- Insulin Levels: Insulin levels drop significantly, making it much easier for the body to burn stored fat for energy.
- Growth Hormones: Levels of growth hormones, which help preserve muscle mass, increase simultaneously.
- Cellular Repair: The body initiates a "refresh" of the entire system by removing old cells and toxins.
Pros and Cons
Many people choose dietary restriction over intense exercise because it often feels more manageable. While IF offers accessible methods for everyone, it is crucial to be mindful of potential side effects.
Pros:
- It is often simpler than traditional dieting as you don’t necessarily need to count every calorie.
- It promotes weight loss by lowering insulin and boosting fat burning.
- It can help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- It encourages the growth of new brain cells and improves memory.
Cons:
- Initially, hunger can be difficult to manage, leading to overeating or bingeing during the eating window.
- In some women, extreme fasting can cause hormonal shifts and irregular menstrual cycles.
- Side effects such as headaches, irritability, and fatigue are common results of hunger during the fasting hours.
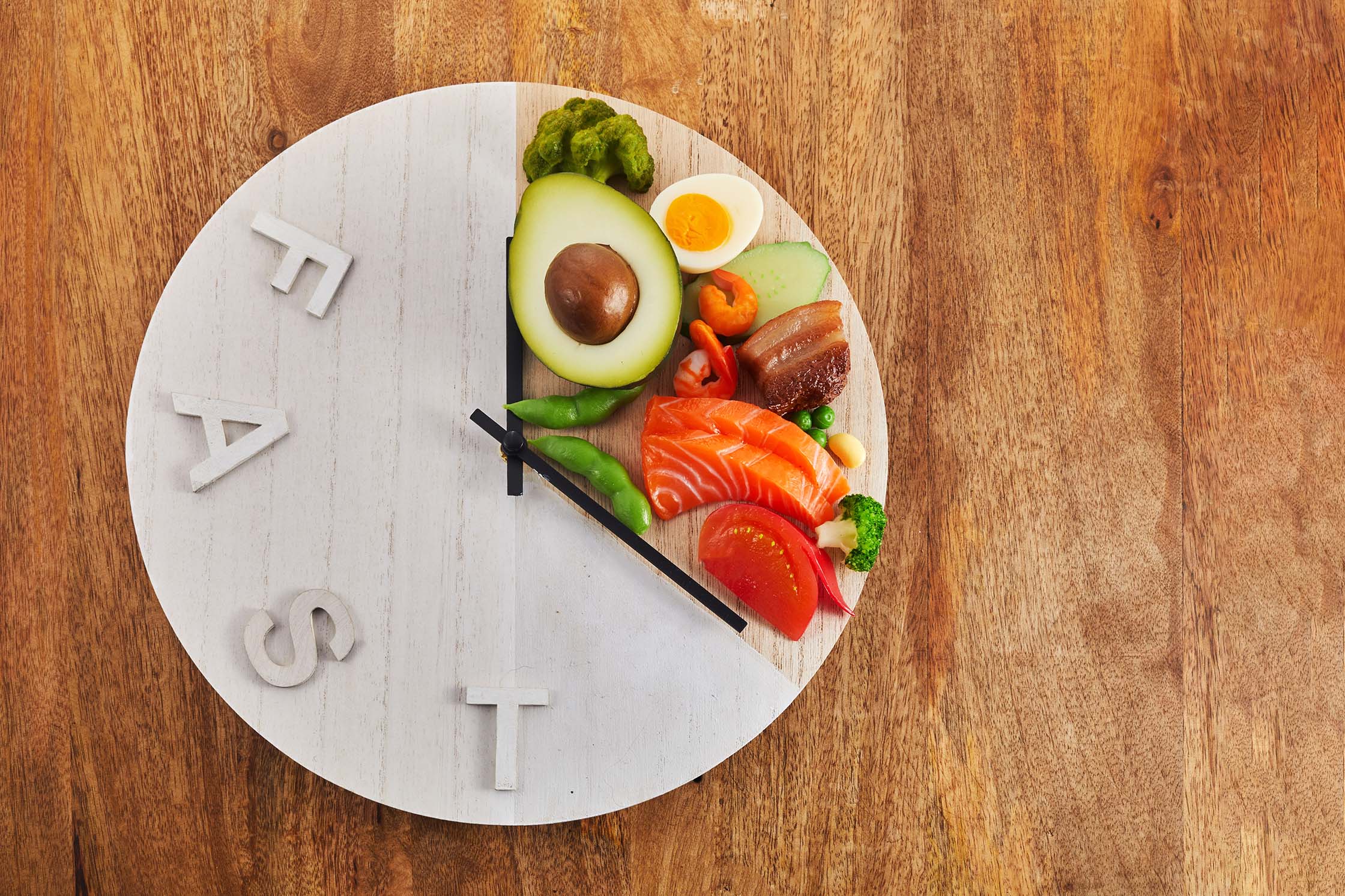

The Correct Way to Fast
To achieve effective results without harming your body:
Start Gradually: Begin with a 12-hour fast and slowly increase it to 16 hours.
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water during fasting periods to stay full. Plain coffee or milk (in moderation) can also be consumed.
Monitor Calories: During the 8-hour eating window, be careful not to exceed your daily calorie limit with excessive fats or sweets.
Prioritize Nutrients: Focus on nutrient-dense foods like meat, fish, and vegetables instead of instant or processed meals.
Align with Rest: It is best to fast during the night when the body is resting. For instance, eating from 8 PM to 4 AM is not recommended just to meet the 8-hour window.
Listen to Your Body: Always observe your body’s reaction. If you experience extreme dizziness or exhaustion, stop immediately and consult a professional doctor.
Intermittent Fasting is not a "quick fix" for instant results; it is a disciplined, long-term investment in your health. By paying attention to your body's signals and following a systematic approach, you can truly achieve a healthier and more energetic lifestyle.




Comments